Table of Contents
ToggleQuick Bio Understanding HCOOCH CH2 H2O
| Term | Meaning | Role in Chemistry |
|---|---|---|
| HCOOCH | Methyl formate, the methyl ester of formic acid | Reactant in hydrolysis and organic synthesis |
| CH2 | Methylene group, basic unit in organic molecules | Acts as a bridge or reactive site in molecules |
| H2O | Water, universal solvent | Participates in reactions like hydrolysis and bond cleavage |
Understanding HCOOCH CH2 H2O: A Quick Guide
HCOOCH CH2 H2O may look like a chemical formula but it is not a single molecule. Instead, it is a combination of chemical fragments HCOOCH, CH2, and H2O used to describe chemical systems and reactions in organic chemistry. Understanding these parts helps learners see how molecules interact in lab experiments and industrial processes.
What “HCOOCH CH2 H2O” Means
The term HCOOCH CH2 H2O represents a system rather than a fixed compound. HCOOCH is shorthand for methyl formate, CH2 is a methylene group, and H2O is water. Together, they illustrate how these molecules behave in chemical reactions, especially hydrolysis reactions where esters break down in water to form acids and alcohols.
Breaking Down HCOOCH – Methyl Formate
HCOOCH refers to methyl formate (HCOOCH3), the simplest formate ester. It is formed when formic acid (HCOOH) reacts with methanol (CH3OH). Methyl formate is a colorless liquid with a fruity smell. It is widely used as a solvent, in organic synthesis, and as an intermediate in producing chemicals like formic acid and methanol. Its reactive ester bond is crucial in the reactions described by HCOOCH CH2 H2O.
CH2 – The Methylene Group
The CH2 in HCOOCH CH2 H2O is a methylene group, a carbon atom bonded to two hydrogens. It is one of the most common building blocks in organic chemistry. CH2 units appear in long-chain molecules, act as bridges between functional groups, and provide reactive sites in addition or substitution reactions. In systems described by HCOOCH CH2 H2O, methylene plays a structural and reactive role.
H2O – Water’s Role
H2O (water) is essential in chemistry. In the context of HCOOCH CH2 H2O, it participates as a reactant, not just as a solvent. Water can attack chemical bonds, such as the ester bond in methyl formate, to produce hydrolysis products. Water’s polarity and nucleophilic nature make it a key player in reactions that transform organic compounds.
Chemical Reactions Involving HCOOCH CH2 H2O
One of the main reactions involving HCOOCH CH2 H2O is the hydrolysis of methyl formate. The reaction is:
HCOOCH3 + H2O → HCOOH + CH3OH
Water attacks the carbonyl carbon in the ester, breaking the bond and forming formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol (CH3OH). This is a classic example showing how the fragments of HCOOCH CH2 H2O interact to produce different chemical products.

Acid-Catalyzed and Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis can occur in two ways. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis uses an acid to make the ester more reactive toward water. Base-catalyzed hydrolysis, or saponification, uses a base to break the ester bond, forming an acid salt and alcohol. Both processes show the role of H2O in transforming HCOOCH into simpler molecules.
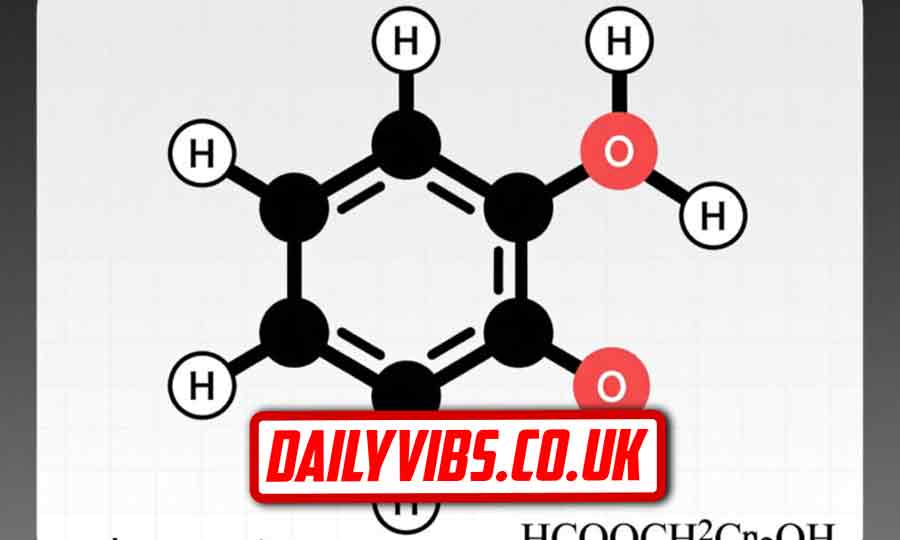
HCOOCH CH2 H2O Chemical Structure Explained
Although HCOOCH CH2 H2O is not a single molecule, its chemical structure components are clear. Methyl formate has a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to an oxygen attached to a methyl group. CH2 is a simple methylene fragment present in many molecules, and H2O is water, which interacts with the ester to enable hydrolysis. Understanding these structures helps predict chemical behavior and reaction outcomes.
Industrial and Laboratory Importance
HCOOCH CH2 H2O is significant in both labs and industry. Hydrolysis reactions are vital in producing carboxylic acids and alcohols, which are used in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and agrochemicals. Methyl formate also serves as a solvent and intermediate in many synthetic processes. Understanding how these components interact allows chemists to design efficient reactions and sustainable processes.
Hydrolysis reactions involving HCOOCH CH2 H2O often use water as a reactant, making them more environmentally friendly than solvent-based methods. Using water reduces toxic waste and allows cleaner, safer reactions in industrial manufacturing. This aligns with modern principles of green chemistry.
Organic Synthesis and Learning Importance
For students, HCOOCH CH2 H2O is a useful example of how chemical notation can describe reactions instead of fixed molecules. Learning about it develops skills to read reaction schemes, understand ester hydrolysis, and recognize the role of water in breaking chemical bonds. It also helps identify how methylene units function in molecular frameworks.
HCOOCH CH2 H2O in Real Reactions
In practice, chemists use HCOOCH CH2 H2O as shorthand to describe hydrolysis or related transformations. The fragments guide predictions on which products will form and how molecules will react. This helps in synthesizing new molecules and designing industrial chemical processes efficiently.
Key Takeaways
- HCOOCH CH2 H2O is a combination of chemical fragments, not a stable single molecule.
- HCOOCH represents methyl formate, the ester undergoing hydrolysis.
- CH2 is a methylene group, crucial in molecular structure and reactivity.
- H2O is water, the nucleophile breaking the ester bond.
- The system illustrates hydrolysis reactions, key in labs and industry.
- Understanding this term improves comprehension of reaction mechanisms and chemical behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
A: HCOOCH CH2 H2O is a combination of chemical fragments representing methyl formate (HCOOCH3), a methylene group (CH2), and water (H2O), commonly used to describe hydrolysis reactions.
Q2: What does HCOOCH CH2 H2O chemical structure mean?
A: It shows the structure of methyl formate (HCOOCH3) and its interaction with water. CH2 indicates a methylene unit important for molecular reactivity.
Q3: How does HCOOCH CH2 H2O react in hydrolysis?
A: In hydrolysis, water attacks the ester bond in methyl formate, producing formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol (CH3OH).
Q4: Where is HCOOCH CH2 H2O used?
A: It is significant in organic synthesis, industrial chemistry, and green chemistry, especially when producing acids, alcohols, and polymers.
Q5: Why is HCOOCH CH2 H2O important for learners?
A: It helps students understand reaction mechanisms, the role of esters, methylene groups, and water in organic chemistry, improving practical knowledge.
Conclusion
Understanding HCOOCH CH2 H2O: A Quick Guide shows that chemistry often uses shorthand to describe interactions, not fixed compounds. HCOOCH CH2 H2O explains how methyl formate reacts with water, forming formic acid and methanol, with methylene groups providing structural context. Learning these interactions gives students and chemists a deeper understanding of organic chemistry, reaction mechanisms, and industrial applications. Mastering HCOOCH CH2 H2O ensures a strong foundation for exploring advanced chemistry topics.
Unlock the full potential of HCOOCH CH2 H2O in your chemistry studies and experiments! Learn more, practice reactions, and explore its industrial uses today. Don’t forget to share this guide with fellow learners and More Visit Dailyvibs subscribe for more in-depth chemistry insights.